Introduction
Lyme disease in dogs is a serious concern for pet owners. This tick-borne illness can cause severe health issues. Understanding its symptoms, prevention, and treatment is crucial to keeping your dog healthy.
1. What is Lyme Disease?
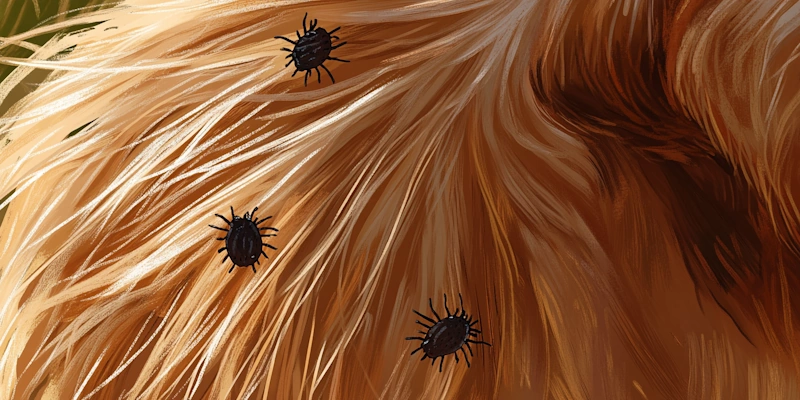
Lyme disease in dogs is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi. Ticks, particularly the black-legged tick, transmit this bacterium. These ticks attach to dogs and transfer the bacteria through their bite.
Moreover, Lyme disease can lead to various health problems. Joint pain, fever, and lethargy are common symptoms. In severe cases, it can cause kidney damage or affect the nervous system.
2. Recognizing Symptoms
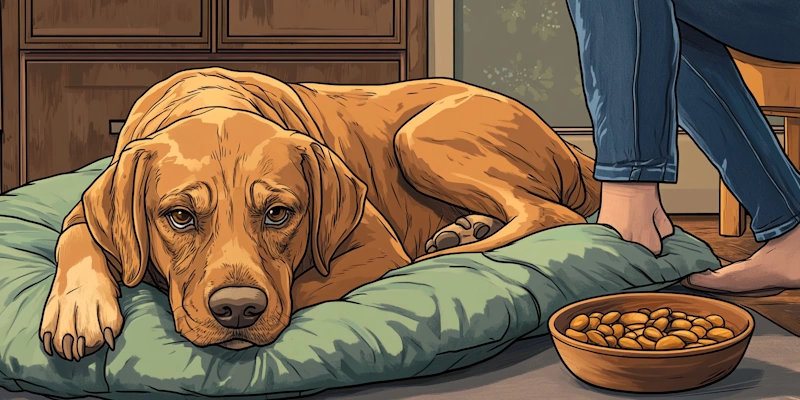

Recognizing Lyme disease in dogs early is crucial for effective treatment. Common symptoms include lameness, swollen joints, and decreased appetite. Some dogs may also develop a fever or show signs of discomfort.
Transitioning from recognizing symptoms to seeking veterinary care is vital. If you notice any unusual behavior, consult your vet immediately. Early diagnosis can prevent more severe complications and ensure a better prognosis.
3. Preventive Measures

Preventing Lyme disease in dogs involves several steps. Regular tick checks are essential, especially after outdoor activities. Removing ticks promptly reduces the risk of infection.
Using tick preventives, such as collars, spot-on treatments, and oral medications, is also effective. These products kill ticks before they can transmit the bacteria. Additionally, keeping your yard clean and tick-free helps minimize exposure.
4. Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing Lyme disease in dogs involves blood tests to detect antibodies. If your dog tests positive, your vet will prescribe antibiotics. The treatment usually lasts several weeks and helps eliminate the bacteria.
Transitioning from treatment to recovery requires close monitoring. Ensure your dog completes the full course of antibiotics. Regular check-ups are necessary to monitor their progress and prevent relapses.
5. Long-Term Care and Management
Long-term care for dogs with Lyme disease involves ongoing vigilance. Even after treatment, some dogs may experience recurring symptoms. Regular vet visits and monitoring are essential.
Additionally, maintaining preventive measures helps avoid future infections. Consistent use of tick preventives and regular checks will keep your dog safe. Educating yourself about the Lyme disease ensures you can act promptly if symptoms reappear.
Conclusion
Lyme disease in dogs is a serious but manageable condition. Understanding its symptoms, prevention, and treatment can keep your pet healthy. Regular vet visits and preventive measures are key to managing this illness.